- Home
- Directory
-
Our Programs
-
Strategic Advocacy Course
- Collaborations
- Humane Education
- International Policy
-
Model Animal Welfare Act
- Get the Book!
- Contents
- Part 1: Guiding Principles - A Broad Overview
- Part 2: Proposal for the Wording of a New Animal Welfare Act
-
Part 3: Explanatory Notes
- Notes to Chapter 1: Preliminary Provisions
- Notes to Chapter 2: General Provisions
- Notes to Chapter 3: Keeping of Animals/Care of Animals
- Notes to Chapter 4: Specific Categories of Animal Use
- Notes to Chapter 5: Implementation and Enforcement Provisions
- Notes to Chapter 6: Penal and Final/Concluding Provisions
- Constitution Project
-
Strategic Advocacy Course
-
Resources
- Events
- About Us
- Blog
- font size decrease font size increase font size
- No comment

Introduction
The Overall Policy Environment
Strategies
Policies
Laws and Regulations
Introduction
An analysis of the policy context for your research is vital to the establishment of an effective advocacy strategy. It should cover: the policy environment; the policy system; and the organizations and people involved.
In advocacy research people often concentrate on the issue, without paying sufficient attention to how power operates, how change happens and how it is sustained. Policy systems and processes are often complex, with varied and different points of entry. People are at the heart of policy-making, whether they are targets, messengers, allies or opponents. If you wish to influence policy change, you need to understand how key institutions (or organizations) work, who the decision-makers are, and how decisions can be influenced.
Key elements of policy context analysis include:
- Identifying the policy related causes of animal issues
- Understanding the structure of policymaking bodies
- Understanding formal and informal policy making processes
- Identifying key actors and institutions (or organizations) that make decisions about policy, as well as those who can influence policy makers
- Analyzing the distribution of political power among key actors
- Understanding the social and political context
Opportunities to influence policy-makers can arise at any time, so where there is advocacy capacity, it is recommended that the political, economic, socio-cultural, and technological environments are monitored to keep abreast of emerging issues and the positions of government and other leaders with respect to these issues.
The Overall Policy Environment
The policy environment includes all aspects surrounding policy-making. This would include the broader socio-economic aspects that are analysed in organizational strategy-making. Important sources for research into this broader policy environment – and what are the pressing concerns of the day - include: the media, research institutes, veterinary bodies, donors, business, and civil society.
|
Advocacy Tool |
The policy-making environment is greatly influenced by the country’s broader socio-economic situation. This will be covered in Module 3 on Strategic Planning for Advocacy. But in your research, it is important to remember to always keep an eye on the broader horizon, to ensure that you are ready and open for opportunities that may influence or change regular policy processes and priorities.
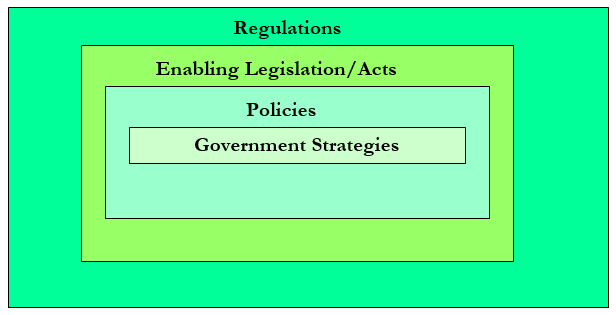
The more narrow governmental policy arena can be depicted diagrammatically as follows:
Key questions to be asked when analyzing the policy environment include:
- What are the animal welfare issues?
- How important are these to both the animals and to society?
- What are the existing strategies, policies and laws that cause or relate to these problems and how are they implemented?
- How could changes in policy help resolve the problems?
- What type of policy change is needed (legislation, proclamation, regulation, legal decision, committee action, institutional practice, or other)?
- What are the financial implications of the proposed policy change?
One aspect of the policy making environment that will have an enormous impact upon your advocacy is the level of openness and transparency. In some open and democratic regimes, it is possible not only to obtain all relevant information through official channels, but also to take part in relevant meetings and consultations. Conversely, in regimes that lack openness and transparency it may be difficult to meet key decision-makers and achieve involvement or consultation (and in some cases even to obtain information through official channels). Advocacy is more likely to be successful in a more democratic and open political system.
Strategies
Investigate the strategies underlying the policies on your issue. If dealing with government, you will find that most governments formulate strategies before taking legislative or administrative action. Strategies will help to identify attitudes, interests and motivations on an issue, as well as future plans.
Policies
Policies form the basis for policy action. They can be international or regional policies (including conventions and agreements), national or organizational.
Research into policies (and policy commitments) can help to identify policy implementation gaps, as well as future plans. Policy research is another important area, as this informs future policy-making. Policy research can be carried out at international, regional, national or local level.
Laws and Regulations
Your research should include any existing laws (acts and regulations) that may affect your issue. Different countries have different legislative systems – see the section below – so these will take different forms.
Once research has identified legislative provisions, it is necessary to go one step further, and to research enforcement.
International standards should be incorporated into national legislation and successfully implemented.
Regional regulations may be directly applicable (as in the case of European Union regulations).